Skin cancers is classified as skin cancer and non-melanoma(NMSC). BCC (Basal cell carcinoma) is one of the two main types of non-melanoma(NMSC). It develops in the basal layer of the epidermis and is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy worldwide.
WHAT ARE THE STEPS FOR APPLICATION ?
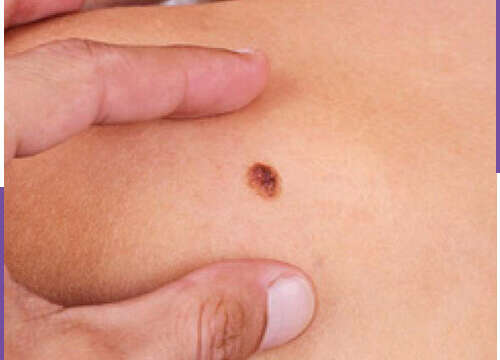
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC) occurs in the basal layer of the epidermis and is the most commonly diagnosed malignancy in the world. There is a 30% lifetime risk in an white skinned person. Cumulative DNA damage and gene mutations resulting from exposure to UV rays are the leading cause of BCC.
The major risk factor for BCC is exposure to ultraviolet (UV) rays from the sun or artificial sources such as solarium. It usually develops slowly and causes local damage. It presents in the form of slow-growing, translucent, protruding nodules in sun-exposed skin areas such as the head and neck, and may occasionally show not only crusting or ulceration in the middle, but also flaked skin spots or enlarged pits or pores. BCC progression is usually characterized by slow growth and minimal invasion of soft tissue; surgical excision can provide full recovery in most cases of BCC. It is rarely metastasised , so its mortality is low. It can progress, especially if it is untreated or if it occurs in a high-risk area, and can lead to widespread damage to the tissue and disfigurement. Cartilage can infiltrate muscle or bone and even spread to the skull.It can cause bodily disfigurement, cause significant morbidity and even be fatal. BCC development in light-skinned individuals is 10-20 times more likely than dark-skinned individuals.
The diagnosis can be made based on clinical features associated with each type of BCC. After the initial examination of the skin, a biopsy sample is taken from the suspicious lesion for differential diagnosis. In order to confirm the clinical diagnosis and start treatment in a timely manner, a biopsy should be performed immediately for suspicious lesions (especially in high-risk areas, such as the middle part of the face). Typically, the BCC follows a relatively quiet course of slow growth and soft tissue, exhibiting only minimal invasion. Consequently, BCC typically has positive prognosis because full surgical excision improves in most cases. However, BCC may recur or progress from time to time, the BCC recurrence rate is about 12%, but this rate may vary depending on the treatment direction.
WHAT ARE THE AREAS FOR THE APPLICATION?
It is applied to all body parts.